WARNING: This article contains graphic content.
For years, animal rights activists have rallied against the use of canines for product testing. Although in some cases, these advocates have succeeded in convincing companies to stop animal testing, the reality is that these people still have a long way to go to fully eradicate this horrendous practice.
Just this week, the Humane Society of the United States uploaded a video on the company Dow AgroScience’s product testing on Beagles and you’ll be horrified to see what they’ve done to these creatures.
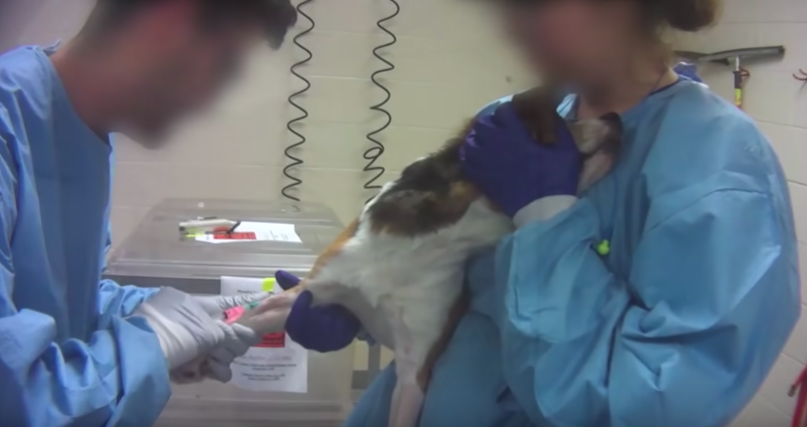
According to the Humane Society’s investigation in the Charles River Laboratories in Mattawan, Michigan, 36 dogs have been chosen to be used for a year-long program that tests the effects of a particular pesticide solution to a canine’s body. This includes force-feeding, injecting, and implanting foreign items into the dogs’ systems. And since these strange items are entering their bodies, these animals are often left with crippling side effects that eventually lead to their deaths.
The HuffPost reports that if these dogs manage to survive the program, they are scheduled to be euthanized in July.
Since the Humane Society uploaded the video on YouTube, Corteva Agriscience released a statement in response to the backlash they’ve received from netizens.
Please read our statement in response to the report published today by the Humane Society of the United States. pic.twitter.com/WO5mEpKTri
— Corteva Agriscience (@corteva) March 12, 2019
Even though the company believes that “there are better ways to attain data,” they will not stop the program until the brand’s counterparts in Brazil no longer requires animal testing.
Watch the video below to see the full extent of their animal testing procedure:
If you’re interested in putting an end to this program, then feel free to sign the Humane Society’s petition here.
___
Read more from InqPOP!:
Oplan ‘Dog-hang’ which aims to get rid of dogs shows how killing is the new normal
PCCI and animal lovers condemn tragic death of 30 dogs at a dog show
WATCH: Dog reunites with owner who has Alzheimer’s Disease


