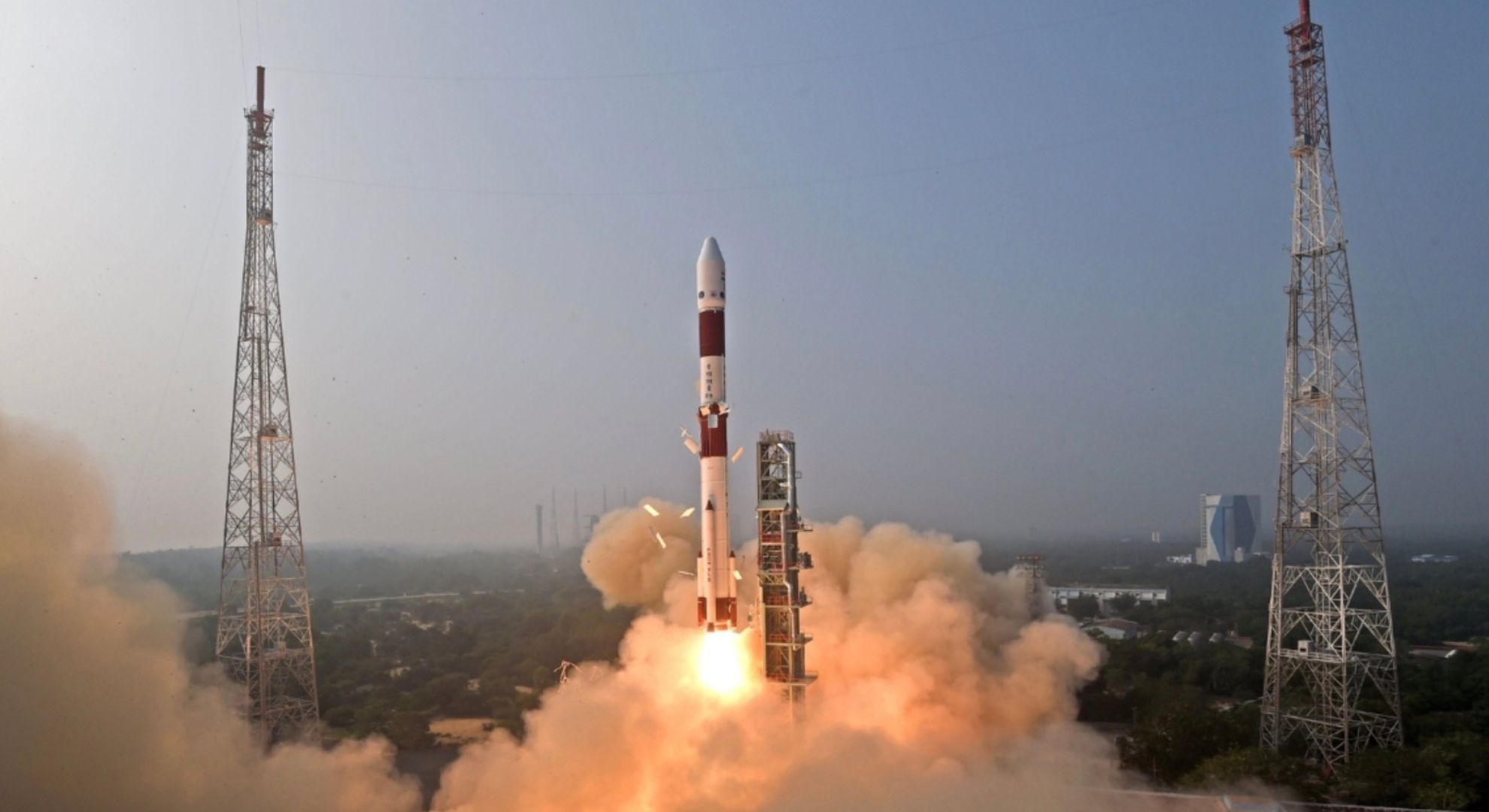
Welcoming the new year on Monday, the Indian Space Research Organisation (ISRO) successfully started its orbital calendar on January 1st, 9:40 AM Indian Standard Time (IST) or 4:10 AM UTC with the launching of a spacecraft as India’s first X-ray astronomy mission that will help better understand the emissions from things like neutron stars, black holes, and more.
The 60th mission of India’s Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle (PSLV) named PSLV-C58 was made possible by a four-stage Polar Satellite Launch Vehicle featuring two solid rocket boosters (PSLV-DL), carrying two spacecraft – the X-ray Polarimeter Satellite (XPoSat) and the PSLV Orbital Experimental Module-3 (POEM-3). The mission is planned to extend for a minimum of five years.
The agency stated that the orbital observatory’s objective is to gain insights into the degree and angle of polarization from celestial bodies; to measure polarization of X-rays in the energy band 8-30keV emanating from about 50 potential cosmic sources through Thomson Scattering by POLIX payload; carry out long term spectral and temporal studies of cosmic X-ray sources in the energy band 0.8-15keV by XSPECT payload; carry out polarization and spectroscopic measurements of X-ray emissions from cosmic sources by POLIX and XSPECT payloads respectively in the common energy band. As stated in the objectives of ISRO’s mission.
ISRO describes XPoSat as “the first dedicated scientific satellites from ISRO to carry out research in space-based polarization measurements of X-ray emission from celestial sources.” as proven by the inclusion of 10 other experimental payloads. The spacecraft is currently orbiting Earth at a low distance of around 600 km.
With ISRO’s success rate of over 95% on 59 missions, PSLV-C58 promises another year of groundbreaking achievement for the agency to also contribute to universal space exploration.
Other POP! stories that you might like:
First human-whale ‘conversation’ could pave the way for communication with aliens, scientists claim
Keeping secrets to yourself can be energizing, says study
Habitation in Mars appears to be a possibility as scientists discover new material
‘AI Death Calculator’ can ‘predict’ when you’ll die, with eerie accuracy
NASA discovers ‘Christmas Tree Cluster’ of stars illuminating in space